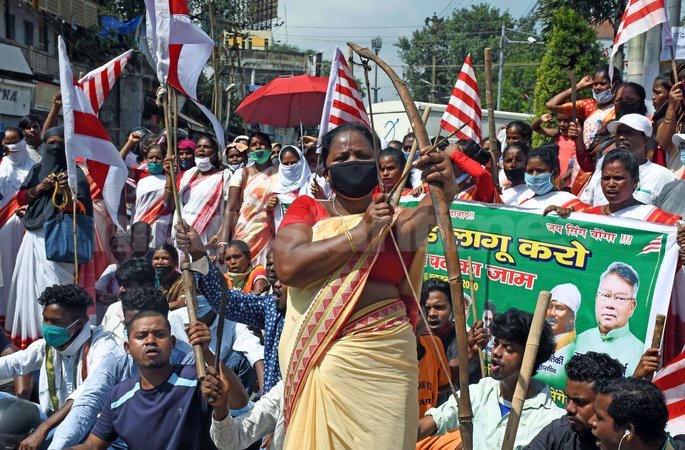
India’s Adivasis (tribal communities) are among the oldest inhabitants of the subcontinent, with rich traditions rooted in nature worship and community life. Yet, their religious identity is often debated, especially when they are officially categorized as “Hindu” in the Census. Many tribal groups reject this classification and demand recognition of their distinct faith under the Sarna Code.
This article explains why tribals resist Hindu identity and what the Sarna Code means for them.
Who are the Adivasis?
- Indigenous communities of India, living mainly in Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, and Northeast India.
- They follow ancestral faiths centered on forests, hills, rivers, and sacred groves (Sarna).
- Their belief systems predate organized religions like Hinduism, Islam, or Christianity.
Why Tribals Reject Hindu Identity
1. Different Religious Practices
Adivasis worship nature, ancestral spirits, and community deities such as Marang Buru (Great Mountain). They do not traditionally follow the Vedas, Hindu gods, or temple rituals.
2. Preserving Cultural Identity
If classified as “Hindu,” their indigenous faiths risk being absorbed into the larger Hindu fold, weakening their unique traditions.
3. No Caste System
Hindu society is structured by caste and varna, but tribal society is clan-based and more egalitarian. Many tribals see Hindu identity as imposing hierarchies alien to their way of life.
4. Political Concerns
Hindu nationalist groups often try to integrate tribals under the Hindu umbrella. Tribal leaders resist, saying this dilutes their cultural and religious independence.
What is the Sarna Code?
- Sarna means “Sacred Grove,” the place where tribals worship nature and spirits.
- Currently, the Census only allows Adivasis to register as Hindu, Christian, Muslim, or Others.
- Sarna Code is the demand for a separate religious category in the Census to officially recognize tribal faiths.
Why is the Sarna Code Important?
- Identity & Survival – Protects indigenous belief systems for future generations.
- Legal Rights – Many welfare schemes and protections depend on official recognition.
- Representation – Acknowledges tribals as followers of a distinct faith, not just a subset of Hinduism.
Conclusion
Tribals reject the Hindu identity because their worldview, practices, and traditions are fundamentally different. The Sarna Code movement is about safeguarding their indigenous religion, culture, and political autonomy. Recognition of Sarna as a separate faith would ensure that India’s tribal heritage continues to thrive without being overshadowed by dominant religions